Do you know about monomer? It’s an important factor in coating emulsions. Do you know What is vinyl acetate monomer? Today, We will discuss vinyl acetate monomer (VAM); some of you may be a bit confused about it. Don’t worry, you will have a basic understanding after reading this article.
Table of Contents
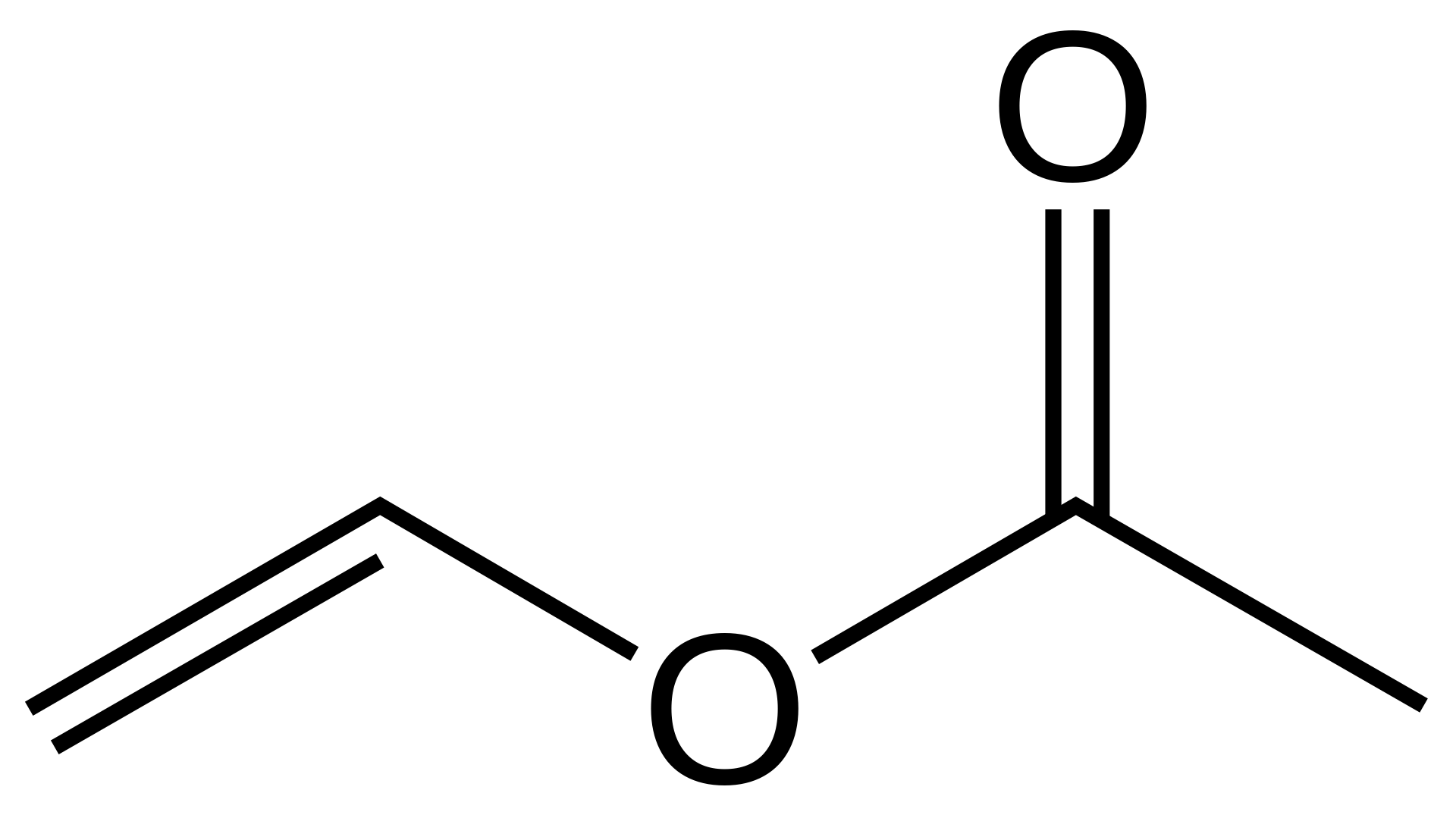
What is Vinyl Acetate Monomer?
A monomer is an organic compound that has not polymerized. It is a direct factor in determining the quality and application of an emulsion. Vinyl acetate monomer (VAM) is an important and economical intermediate. So, it is widely used and used in large quantities.
Vinyl acetate monomer is a volatile, flammable, reactive, colorless liquid. It has a sweet, fruity but pungent smell. Using VAM can produce a variety of polymers and resins. End applications are in the preparation of paints and coatings, adhesives, sealants, etc.
It is not enough for weathering, tensile properties, and crystallinity. VAM coatings are not suitable for outdoor applications due to weak weather resistance. VAM has good flexibility and bonding strength. These two properties make it suitable for the preparation of adhesives.
How is Vinyl Acetate Monomer Polymerized?
Vinyl acetate monomer (VAM) can be polymerized by free radical polymerization. VAM can be polymerized using these three methods: natural, solution and emulsion polymerization. Emulsion polymerization is the most commonly used method. Because it can effectively disperse the monomer in water to form a stable emulsion.
Polymerization reactions typically include the following steps: begin – propagate – finish. It is important to note that the properties of the resulting polymer may be affected by many factors. These factors include reaction conditions, initiators, monomer proportions and other monomers.
What are the Considerations for VAM Storage and Polymerization?
Extremely flammable, vapors may cause flash fires.
There must be attention to the loss of polymerization inhibitors.
Do not allow contact with heat, radiation, oxidizing substances, SiO2, strong acids or bases. Because spontaneous polymerization is easy to occur, the container may rupture or explode.



What is Vinyl Acetate Monomer Used for?
As we mentioned earlier, vinyl acetate-based polymers have a wide range of uses. The polymers can form strong, flexible, adhesive films. It is very suitable for the preparation of adhesives and coatings. They can also be used to produce “rubber-like” materials.
Polyvinyl Acetate (PVA)
Polyvinyl acetate (PVA) is a polymer made by polymerizing vinyl acetate monomers. Polyvinyl acetate is usually available in the form of a white powder. Polyvinyl acetate powder has adhesive properties. And it can be used in adhesives, coatings, textile finishes, etc. Polyvinyl acetate glue is used in bags, envelopes, tape and plastics.
PVA powder converts to polyvinyl alcohol (PVOH) powder when exposed to heat, moisture, or certain chemical reactions. PVOH powder is produced by the hydrolysis of PVA They has different properties, including water solubility and film forming ability.
Vinyl Acetate-ethylene Copolymer (VAE)
Vinyl acetate-ethylene copolymer (VAE) is formed by copolymerizing vinyl acetate monomer with ethylene. VAE copolymers have better properties than polyvinyl acetate. These properties include flexibility, toughness, thermal stability and moisture resistance. Adding ethylene greatly enhances the properties of the resulting copolymers, broadening their applications.
Vinyl acetate-ethylene copolymer keeps the adhesive properties, so it can used to prepare adhesive. It is also used in coatings, textiles, nonwoven adhesives and construction materials.
Ethylene-vinyl Acetate (EVA)
Ethylene vinyl acetate copolymers (EVA) are made by polymerizing vinyl acetate monomer with ethylene. Ethylene addition enhances copolymer flexibility, toughness, and durability. It also improves the copolymer’s low temperature and impact resistance. Higher vinyl acetate content usually improves adhesion. The lower vinyl acetate content improves heat resistance and stiffness.
EVA copolymers are widely spread and used due to their multifunctional properties. They are commonly used in packaging, shoes, wire insulation, automobiles and construction, etc. Ethylene vinyl acetate film, ethylene vinyl acetate glue, ethylene vinyl acetate rubber, ethylene vinyl acetate adhesive, etc. are products made of EVA.
Vinyl Acetate–acrylate Copolymers Emulsion
Vinyl acetate-acrylate emulsion copolymers are copolymers formed by the polymerization of vinyl acetate monomer and acrylic monomer. These copolymers are usually produced in the form of emulsions. The polymer particles are dispersed in the water medium. The emulsion system typically consists of water, emulsifiers and stabilizers. They help to disperse the monomers and form stable polymer particles.
Vinyl acetate-acrylate emulsion copolymers offer adhesion, water resistance, toughness and flexibility properties. The polymerization of these provides balanced properties. Combine the desirable characteristics of acrylic vinyl, such as adhesion, with the benefits of acrylic monomers, such as durability and water resistance. It can be used in vinyl acrylic paint, adhesives, sealants and textile finishing agents.


Infinechem Provides VAE、Vinyl acrylic emulsion、PVA/PVOH Powder
VAE (vinyl acetate-ethylene copolymer) emulsion:
IFC-7205, IFC-2902, IFC-2901, IFC-2904, IFC-2906
PVA/PVOH (polyvinyl alcohol) powder:
Vinyl acrylic emulsion: IFC-1128
We have a specialized R&D team that is constantly developing new products. Feel free to contact us, we can meet your needs and make your program more sustainable.

